| Section-A | 16 to 280 inch |
|---|---|
| Section-B | 20 to 850 inch |
| Section-C | 35 to 850 inch |
| Section-D | 85 to 850 inch |
| Section-E | 150 to 850 inch |
| Section-F | 180 to 850 inch |
| Section-SPZ | 630 to 3350 mm |
| Section-SPA | 800 to 4500 mm |
| Section-SPB | 1600 to 8000 mm |
| Section-SPC | 1600 to 20000 mm |
| Section-8V | 135 to 850 inch |
| Section-Conical | 65 to 800 inch |
What is V-belt?
V-belts are a type of power transmission belt with a trapezoidal cross-section, commonly used in industrial and automotive applications to transfer power from one pulley to another. They are known for their efficiency, reliability, and ease of use. The technology behind V-belts has evolved over the years to enhance their performance and durability. Here are some key aspects of V-belt technology:
Material: V-belts are typically made from rubber or synthetic materials, such as neoprene, which provide flexibility, wear resistance, and resistance to environmental factors.
Cord Construction: The cords inside V-belts play a crucial role in transferring power. They are often made of materials like polyester or aramid, and their arrangement, tension, and construction contribute to the belt's strength and flexibility.
Compound Formulations: The rubber compound used in V-belts may include additives to improve resistance to heat, oil, abrasion, and other environmental factors. Different formulations are designed for specific applications and operating conditions.
Cord Arrangements: The arrangement of cords within the belt, such as the angle and spacing, influences the belt's flexibility and Load-carrying capacity.
Belt Profiles: V-belts come in various profiles, including classical V-belts (A, B, C, D, E,F etc.), narrow V-belts (SPZ, SPA, SPB, SPC, 3V, 5V, 8V), Pentagonal V- Belt (C) and specialty profiles. Each profile is designed for specific load and speed requirements.
Maintenance-Free Designs: Some V-belts are designed to be maintenance- free, reducing the need for re-tensioning over time. Self-tensioning systems and materials with low elongation contribute to this feature.
High-Temperature Resistance: Advanced V-belt technologies may include features to enhance resistance to high temperatures, making them suitable for applications where heat is a factor.
Precision Engineering: The manufacturing processes for V-belts involve precision engineering to ensure consistent dimensions, which is crucial for proper functioning and compatibility with pulley systems.
It's important to note that advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques continue to drive improvements in V-belt technology. When selecting V-belts for specific applications, it's recommended to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and specifications for optimal performance.
V-Belt Construction :
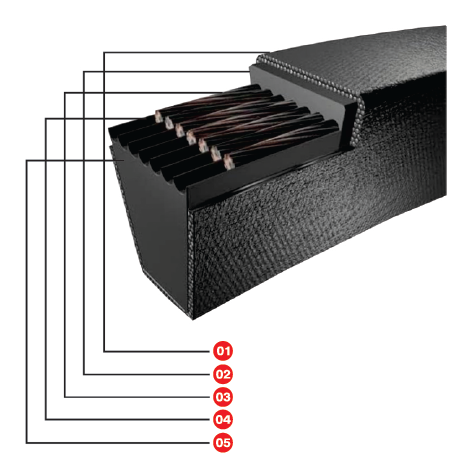
01. Polyester Cotton Jacket :
The cover is impregnated with a specially formulated neoprene synthetic rubber to ensure superior flexibility, better traction and high resistance to wear, oil, heat and staticcharge.
02. Topping Rubber :
This withstands bending stress without fatigue.
03. HMLS Reinforcing Cords :
These high modules and low stretch polyester cords ensure higher power transmitting capacity and enable the belts to carry higher loads with minimum stretch.
04. Adhesive Rubber :
The specially formulated synthetic rubber ply gives required adhesion to the cords, dissipates heat, resist frictions between cords and maintain cushioning effect.
05. Base Rubber :
Specially designed stiff yet flex crack resistant Compound. Maintains an even distribution of the load in the cord layer, preventing power loss and premature belt failure.
Features & Advantage :
ROYAL PREMIUM MAGNUM V-Belts are match free belt subject to precise length control, do not require matching & any number of belts of the same size can be used to make a set.
| Cross Section | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belt Designation | Top Width (mm) | Height (mm) | Small Pully Diameter (mm) | |
| Classic V-Belt | A | 13 | 8 | 71 |
| B | 17 | 11 | 112 | |
| C | 22 | 14 | 180 | |
| D | 32 | 19 | 355 | |
| E | 38 | 23 | 500 | |
| F | 50 | 30 | 700 | |
| Wedge V-Belt | SPZ | 10 | 8 | 63 |
| SPA | 13 | 10 | 90 | |
| SPB | 16 | 13 | 140 | |
| SPC | 22 | 18 | 224 | |
| 8V | 25.5 | 23 | 335 | |
Dimensions of V-Belt :
Classic V-Belt
| image | Cross Section | A | B | C | D | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Top (mm) | 13 | 17 | 22 | 32 | 38 | 50 |
| Height (mm) | 8 | 11 | 14 | 19 | 23 | 30 | |
| Angle (in degree) | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
Wedge V-Belt
| image | Cross Section | SPZ | SPA | SPB | SPC | 5V | 8V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Top (mm) | 10 | 13 | 17 | 22 | 16 | 25.5 |
| Height (mm) | 8 | 10 | 14 | 18 | 13.5 | 23 | |
| Angle (in degree) | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
Banded V-Belt
| image | Cross Section | HB | HC | HD | HE | HSPB | HSPC | H8V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Top (mm) | 17 | 22 | 32 | 38 | 17 | 22 | 25.5 |
| Height (mm) | 14.5 | 17.5 | 22.5 | 26.5 | 17.5 | 21.5 | 26.5 | |
| Angle (in degree) | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
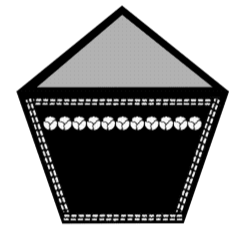
Pentagonal V-Belt
| image | Top Width | Top Height | Bottom Height | Angle (in degree) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
22 mm | 13.5 mm | 14 mm | 40 |

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)